Acupuncture
Choosing Your Acupuncturist
With 5,000 years of history, Acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine is one of the oldest health disciplines in the world. In Western cultures, Acupuncture and TCM has surged in popularity over the past decade, creating excellent opportunities for graduates of this unique diploma program.
As a complete health care system, TCM includes acupuncture, Chinese herbology, diet therapy, tuina and specific exercises such as qigong (Chi-gong) and tai chi.
Acupuncturists view diseases and health disorders as an imbalance in the body’s energy, which flows along well-defined pathways called meridians. By inserting very thin acupuncture needles at specific points along these meridians, a well-trained acupuncturist can normalize the flow of energy and prevent or treat illness by initiating the body’s own healing mechanisms.
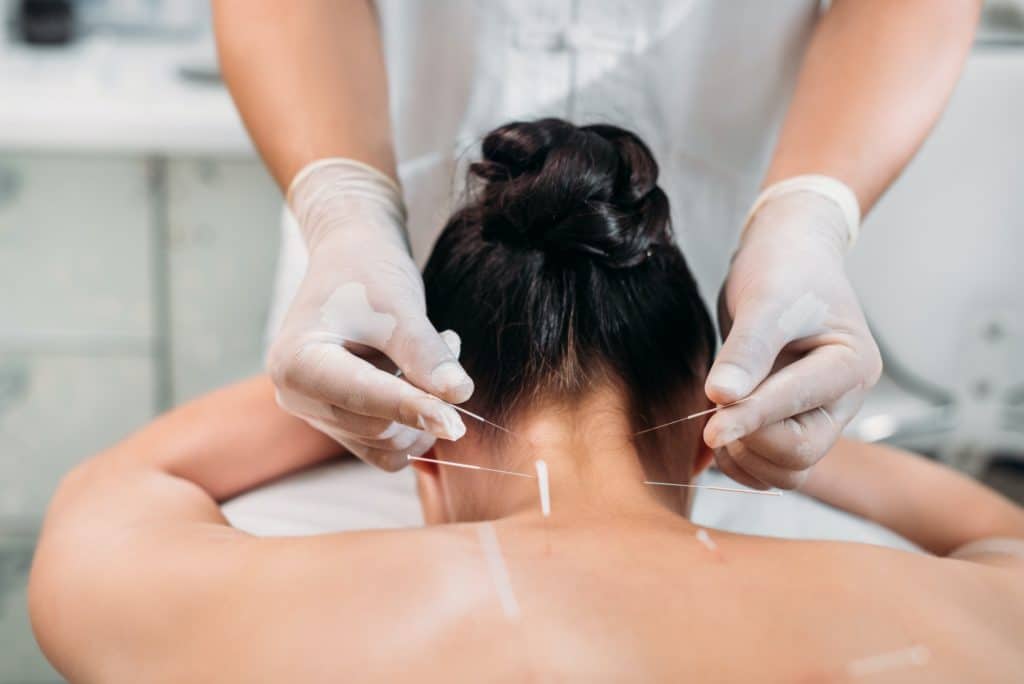

Modern scientific study has confirmed that acupuncture induces biochemical changes in the body that have beneficial effects and can reduce recovery times by up to 50% compared to conventional Western approaches. (Grant MacEwan College)
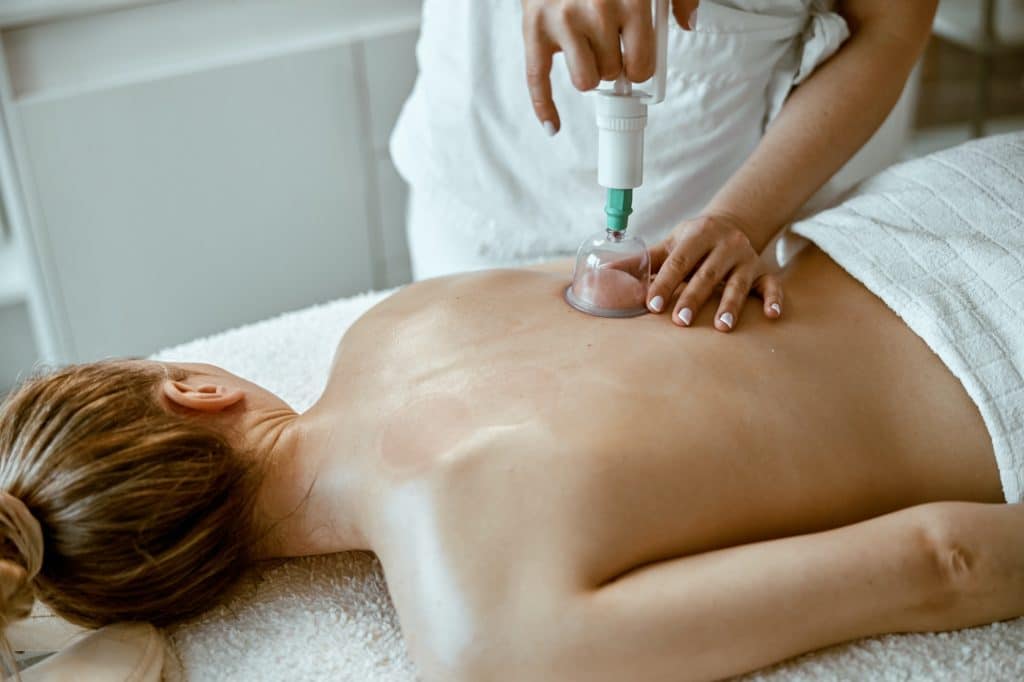
Auricular acupressure does not require the use of needles and therefore is non-invasive. The practitioner may apply pressure with the use of a specialized tool. In addition, tiny seeds are put on a small adhesive (band-aid type) square less than a centimeter wide.
These are then applied to acupuncture points on the ear. Auricular acupressure is effective for chronic fatigue, anxiety, headaches, weight loss, quitting smoking, and more.
Conditions recommended for Acupuncture by the World Health Organization:
- Diseases of cardiovascular system (e.g., coronary heart disease, palpitation, hypertension, dizziness)
- Diseases of the digestive system (e.g., abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, hiccups, abdominal distension, diarrhoea, constipation, irritable bowel syndrome)
- Diseases of urogenital system (e.g., urinary tract infection, seminal emission (wet dreams), impotence, infertility (male), chronic prostatitis)
- Diseases of the nervous system (e.g., headache, migraine, depression, menopause, insomnia, poor memory, sciatica, Parkinson’s syndrome, senile dementia)
- Gynecopathy (e.g., menoxenia, amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, sterility (female)
- Dermatosis (e.g., eczema, shingles, neurodermatitis) Eye-Ear-Nose Diseases (e.g., myopia, sty, sinus problem, deafness, tinnitus)
- All types of pain
- Childhood problems (e.g., restless sleep, poor digestion, cold/flu, infantile autism, hyperactivity)
Types of Traditional Chinese Medicine available:
- Electrical Acupuncture
- Auricular Therapy
- Cupping Therapy
- Facial Rejuvenation
- Chinese Herbal Medicine
- Moxabustion acupuncture and traditional chinese medicine
- Gua sha

Auricular Acupressure
Auricular acupressure does not require the use of needles and therefore is non-invasive. The practitioner may apply pressure with the use of a specialized tool. In addition, tiny seeds are put on a small adhesive (band-aid type) square less than a centimetre wide. These are then applied to acupuncture points on the ear.
Auricular acupressure is effective for Chronic Fatigue, Anxiety, Headaches, Weight Loss, Quitting Smoking, and more.
After an auricular acupressure treatment, it is recommended that you keep the adhesive squares in position for 2 – 4 days. Clients are advised to gently massage the squares with their finger tips approximately five (5) times per day to stimulate the points and enhance the treatment.
Occasionally, clients may experience some ear tenderness or pain and rarely, uncomfortable sensations such as palpitations and nausea. Should these side effects occur, simply remove the adhesive squares from the ear and the unpleasant feelings will stop.
Conditions recommended for Acupuncture by the World Health Organization:
- Respiratory Diseases
- Acute sinusitis
- Acute rhinitis
- Common cold
- Acute tonsillitis
- Gastrointestinal Disorders
- Gastrointestinal disorders
- Bronchial asthma




- Eye Disorders
- Cataract (without complications)
- Myopia
- Central retinitis
- Disorders of the Mouth Cavity
- Acute gingivitis
- Toothache
- Pain after tooth extraction
- Pharyngitis

- Neurologic Disorders
- Headache
- Migraine
- Trigeminal neuralgia
- Facial paralysis
- Paralysis after apoplectic fit
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Paralysis caused by poliomyelitis
- Meniere’s syndrome
- Neurogenic bladder dysfunction
- Nocturnal enuresis
- Intercostal neuralgia
- Orthopedic Disorders
- Periathritis humeroscapularis
- Tennis elbow
- Sciatica
- Low back pain
- Rheumatoid arthritis

